Assam Secondary TET (2012-13) Paper – II (Science) Syllabus
Assam Secondary TET (2012-13) Syllabus for Paper – II (Science Stream). The Teachers Eligibility Test for Secondary Education in Assam is an important examination for direct recruitment of graduate teachers. Find below the full Paper -II (Science Stream) syllabus for Secondary TET 2012-13. This syllabus is standard Higher Secondary Level (Final Year). In case of Part III, candidates are required to choose from either Mathematics or Biology.
ASSAM SECONDARY TET (2012-13) PAPER – II (SCIENCE STREAM) SYLLABUS
PART I: PHYSICS (35 Marks)
- ELECTROSTATICS: i) Electric charges and their conservation. Coulomb’s law– force between two point charges, forces between multiple charges; superposition principle and continuous charge distribution. Electric field, electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines; electric dipole, electric field due to dipole; torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field. II) Electric flux, statement of Gauss’s theorem uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside). iii) Electric potential, potential difference, electric potential due to a point charge, a dipole and system of charges; equipotential surfaces. iv) Capacitors and capacitance, combination of capacitors in series and in parallel.
- CURRENT ELECTRICITY: i) Electric current, flow of electric charges in a metallic conductor, drift velocity and mobility, and their relation with electric current; Ohm’s law, electrical resistance, electrical energy and power. Series and parallel combinations of resistors. ii) Kirchhoff’s laws and simple applications. Wheatstone bridge, metre bridge.
- MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM: i) Concept of Magnetic field, Oersted’s experiments. ii) Biot-Savart law and its applications to current carrying circular loop. iii) Ampere’s law. iv) Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields. v) Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field. vi) Force between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of ampere. Torque experienced by a current loop in a magnetic field; moving coil galvanometer– conversion to ammeter and voltmeter. vii) Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment. Magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron.
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENTS: i) Electromagnetic induction; Faraday’s law, induced emf and current; Lenz’s Law, Eddy currents. Self and mutual inductance, Alternating currents, peak and rms value of alternating current/voltage; reactance and impedance.
- ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES: Electromagnetic waves and their characteristics. Transverse nature of electromagnetic waves, Electromagnetic spectrum.
- OPTICS: i) Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula. Refraction of light, total internal reflection and its applications, refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, thin lens formula, lensmaker’s formula. Magnification, power of a lens, combination of thin lenses in contact. Refraction and dispersion of light through a prism. ii) Microscopes and astronomical telescopes (reflecting and refracting) and their magnifying powers. iii) Wave optics : Wavefront and Huygens’ principle, reflection and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wavefronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygens’ principle. iv) Interference, Young’s double slit experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources and sustained interference of light. Diffraction, Polarisation, plane polarised light; Brewster’s law.
- DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION: i) Photoelectric effect; Einstein’s photoelectric equation– particle nature of light. ii) Matter waves– wave nature of particles, de Broglie relation.
- ATOMS AND NUCLEI : Alpha– particle scattering experiment; Rutherford’s model of atom; Bohr model, energy levels, hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of nucleus, atomic masses, isotopes, isobars; isotones. Radioactivity– alpha, beta and gamma particles/rays and their properties; radioactive decay law. Mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number; nuclear fission and fusion.
- ELECTRONIC DEVICES : Semiconductors; semiconductor diode– I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as a rectifier; I-V characteristics of LED. Junction transistor, transistor action, characteristics of a transistor, transistor as an amplifier (common emitter configuration) and oscillator.
PART II: CHEMISTRY(35 Marks)
- SOLID STATE: Classification of solids based on different binding forces: molecular, ionic, covalent and metallic solids, amorphous and Crystalline solids (e1ementary idea).
- SOLUTIONS: Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, colligarive properties.
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY: Redox reactions; conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity variations or conductivity with concentration, Kohlrausch’s Law, electrolysis and laws of electrolysis (elementary idea), dry cell – electrolytic cells and Galvanic cells; lead accumulator, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, Nernst equation and its application to chemical cells, fuel cells; corrosion.
- CHEMICAL KINETICS: Rate of a reaction (average and instantaneous), factors affecting rates of reaction: concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction; rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half life (only for zero and first order reactions); concept of collision theory (elementary idea, no mathematical treatment).
- SURFACE CHEMISTRY: Adsorption : Physisorption and chemisorption; factors affecting adsorption of gases on solids; catalysis: homogenous and heterogeneous, activity and selectivity: enzyme catalysis; colloidal state: distinction between true solutions, colloids and suspensions; lyophillic, lyophobic multimolecular and macromolecular colloids; properties of colloids; Tyndall effect, Brownian movement, electrophoresis, coagulation; emulsions – types of emulsions.
- P-BLOCK ELEMENTS: Group 15 elements : i) General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, oxidation states, trends in physical and chemical properties; nitrogen. ii) Group 16 elements : General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurence, trends in physical and chemical properties; dioxygen :Group 17 elements : General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties; compounds of halogens: pneparation, properties and uses of chlorine and hydrochloric acid, interhalogen compounds, oxoacids or halogens (structures only).
- D AND F BLOCK ELEMENTS: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first row transition metals– rnetallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation. Preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4.
- COORDINATION COMPOUNDS: Coordination compounds : Introduction, ligands, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, bonding; isomerism, importance of coordination compounds (.in qualitative analysis, exrraction of metals and biological systems).
- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS: i) Alcohols : Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only); identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols; mechanism of dehydration, uses, some important compounds– methanol and ethanol. ii) Phenols : Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophillic substitution reactions, uses of phenols. iii) Ethers : Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses.
- ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS: Carboxylic acids : Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses.
- ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN: Amines : Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Cyanides and Isocyanides will be mentioned at relevant places in context.
- BIOMOLECULES: i) Carbohydrates : Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccharides (glucose and fructose), oligosac charides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen) and importance. ii) Proteins : Elementary idea of a – amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides, proteins, primary’ structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure and quaternary structure (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins; enzymes. iii) Vitamins : Classification and functions. iv) Nucleic Acids : DNA and RNA.
- POLYMERS: Classification : Natural and synthetic, methods of polymerization (addition and condensation), copolymerization. Some important polymers: natural and synthetic like polythene, nylon, polyesters, bakelite, rubber.
- CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE: (1) Chemicals in medicines– analgesics, tranquilizers, antiseptics, disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids, antihistamines. (2) Chemicals in food– preservatives, artificial sweetening agents. (3) Cleansing agents – soaps and detergents, cleansing action.
PART III BIOLOGY (30 Marks)
- Reproduction in Organisms : (i) Asexual Reproduction; (ii) Sexual Reproduction.
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants : (i) Flower-A fascinating Organ of Angiosperms; (ii) Pre-fertilization: Structures and Events; (iii) Double Fertilization; (iv) Post-fertilization: Structures and Events.
- Human reproduction : (i) The Male Reproductive System; (ii) The Female Reproductive and Implantation; (iii) Gametogenesis; (iv) Menstrual Cycle; (v) Fertilization and Implantation; (vi) Pregnancy and Embryonic Development; (vii) Parturition and Lactation.
- Reproductive Health : (i) Reproductive Health-Problems and Strategies; (ii) Population Explosion and Birth Control; (iii) Medical Termination of Pregnancy; (iv) Sexually Transmitted Diseases; (v) Infertility.
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation : (i) Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance; (ii) Inheritance of One Gene; (iii) Inheritance of Two Genes; (iv) Sex Determination; (v) Mutation; (vi) Genetic Disorders.
- Evolution : (i) Origin of Life; (ii) Evolution of Life Forms- A Theory; (iii) Evidences for Evolution; (iv) Adaptive Radiation; (v) Biological Evolution; (vi) Mechanism of Evolution; (vii) A Brief account of Evolution; (viii) Origin and Evolution of Man.
- Human Health and Diseases: (i) Common Diseases in Humans; (ii) Immunity; (iii) AIDS; (vi) Cancer; (v) Drugs and Alcohol Abuse.
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production: (i) Animal Husbandry; (ii) Plant Breeding; (iii) Single Cell Proteins; (iv) Tissue Culture.
- Biotechnology; Principles and Processes: (i) Principles of Biotechnology; (ii) Tools of recombinant DNA Technology; (iii) Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology.
- Ecosystems : (i) Ecosystem- Structure and Function; (ii) Productivity; (iii) Decomposition; (iv) Energy Flow; (v) Ecological Pyramids; (vi) Ecological Succession; (vii) Nutrient Cycling; (viii) Ecosystem Services.
- Biodiversity and Conservation: (i) Biodiversity; (ii) Biodiversity and Conservation; (iii) National Park and Sanctuaries of Assam with special reference to conservation of endangered species.
- Bio resources of Assam: (i) Medicinal and Timber Yielding plants; (ii) Sericogenic Resources (Muga and Eri).
- Environmental Issues: (i) Air Pollution and its Control; (ii) Water Pollution and its Control; (iii) Solid Wastes; (iv) Agro-chemicals and their effects; (v) Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming; (vi) Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere; (vii) Degradation by Improper Resource Utilization and Maintenances; (viii) Deforestation.
PART III MATHEMATICS (30 Marks)
- Relations and Functions: Types of relations : Reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto functions, composite functions, inverse of a function. Binary operations.
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions: Definition, range, domain, principal value branches.
- Matrices: Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew symmetric matrices. Addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication of matrices, simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. Non-commutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix (restrict to square matrices of order.
- Determinants: Determinant of a square matrix (up to 3 × 3 matrices), properties of determinants, minors, co-factors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix.
- Continuity and Differentiability: Continuity and differentiability, derivative of composite functions, chain rule, derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, derivative of implicit function. Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions and their derivatives. Logarithmic differentiation. Derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second order derivatives.
- Integrals: Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, only simple integrals of the type.
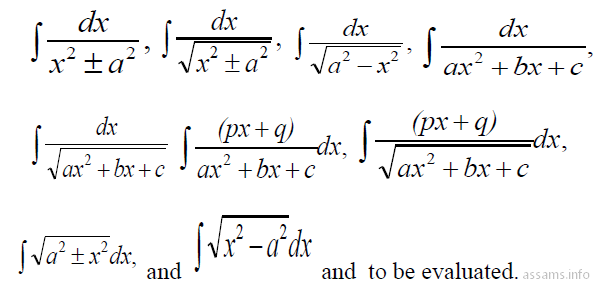
- Definite integrals as a limit of a sum. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (without proof). Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
- Differential Equations: Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Formation of differential equation whose general solution is given. Solution of differential equations by method of separation of variables, homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions of linear differential equation of the type: dy/dx + Py =Q, where P and Q are functions of x.
- Vectors: Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines/ ratios of vectors. Types of vectors (equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Scalar (dot) product of vectors, projection of a vector on a line. Vector (cross) product of vectors.
- Three-dimensional Geometry: Direction cosines/ ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian and vectors equation of a line, coplanar and skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Cartesian and vector equation of a plane. Angle between (i) two lines, (ii) two planes, (iii) a line and a plane. Distance of a point from a plane.
- PROBABILITY: Multiplication theorem on probability, Conditional probability, independent events, total probability.
The Secondary TET is a must for recruitment of graduate teachers in Assam. The Assam Secondary TET exam consists of two papers: Paper – I and Paper – II. The Paper I is common for all candidates, while the Paper II will come in three variations for three streams – Science, Arts and Commerce. Each paper will carry 100 marks. So, the total marks of Assam Secondary TET will be 200. Assam Portal requests candidates to read this Assam Secondary TET (2012-13) Science Paper -II syllabus carefully.
